View Invasion of Poland and over 3,000,000 other topics on Qwiki.
"I did frequently refer to my war record in World War II, but not in any flamboyant way."
George McGovern
George McGovern
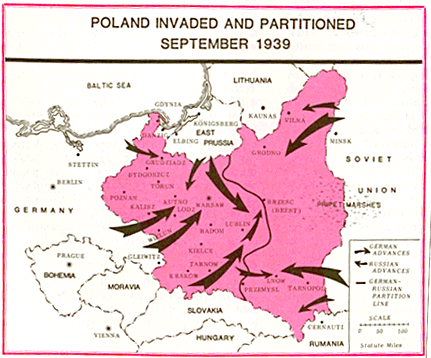
The Invasion of Poland
- Sept. 1, 1939 by Germany
- European Conflict
- German attack using Blitzkrieg warfare (Panzers, Lightnening War) - drivng deep behind enemy lines and encircle enemies and limit enemy supplies
- Captured many troops
- Planes, Tanks, Mechanization are used
- Britain and France declared war on Sept 3 1939
- Russia joins and occupies Eastern half of Poland on 17th September 1939
- War ends on 29 September 1939
The Phony War
- The term describes the lack of action after Invasion of Poland
- Ends in April, 1940
- During this time, the 'Winter War' between Finland and Russia
- 300,000 Russians dead because Finland used Winter Warfare but Russians won
- French make small attack into the Saarland(Germany)
Summary
Germany used the Blitzkrieg tactics on Poland and succeeded. Britain and France declared war on Germany on Sept 3 1939. But they had no action after they declared the war so this time is called the Phony War.